- Tips
- technology
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Tests
- mAh capacity
- Rated Capacity
- everActive
- comparison
- Durability of rechargeable batteries
- Efficiency of rechargeable batteries
- battery voltage
- Accumulated energy
- Batteries vs rechargeable batteries
- LR03 AAA
- LR6 AA
- eneloop
- AG13 LR1154 LR44
- Delta V
- Charge Cycles
- internal resistance
- charge level
- CR 2032
- memory effect
- accredited test
- SR44 357
- Hearing Batteries 675
- SR626 377
- Watch Batteries
- Polarity
- Mah
- passivation
- LS 14250
- LS 14500
Zinc-air hearing aid batteries - what are they, how to care for them, what are they better at?
Back to: List of articles about hearing aid batteries
The battery is covered with a sticker, the removal of which activates the battery. The sticker prevents the battery from drying out, and after removing it, it is gradually discharged. The sticker covers the holes that allow air to flow inside the faucet. Air plays an important role in the production of molecules on the surface of the cathode (the porous membrane inside the battery). The resulting molecules travel to the anode in the form of a zinc gel/powder. As a result of subsequent reactions, electrons are released, which are already set in motion with electricity. The current generated in this way can power the device.
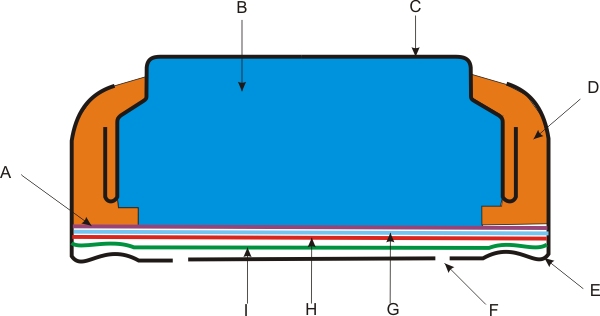
A - separator, B - zinc gel/powder with electrolyte, C - anode housing, D - insulator, E - cathode housing, F - air holes, G - cathode catalyst, H - air distribution coating, I - semi-permeable membrane
Because air is drawn from the environment, it has been possible to reduce the size of the battery while maintaining high performance. Hearing aids and implants require a relatively large amount of energy (more than, for example, watches that use batteries of similar size), so this is where zinc-air batteries have found their way in. If you are interested in additional aspects in the field of electrochemistry, we are here to help :)
Life of zinc-air hearing batteries
Of course, there is no simple answer to what is the life of a zinc-air battery. What is certain, however, is that they are much more efficient than batteries, which have a cathode inside a "button" (not air), so there is much less zinc in them. How long the battery will last depends primarily on the nature and intensity of its use, including the level of hearing impairment. Amplifying the sound by a higher amount requires more energy. The size of the battery also matters. Large batteries (size 675) will last longer than smaller batteries (size 10). In the conducted research, life times for a size 10 battery were achieved at the level of up to 10 days. For the 312 battery, it was up to 12 days. For 13 batteries, it was up to 14 days. However, for the 675 battery it was up to 20 days (1). The batteries range in capacity from 90-105 mAh for size 10 to 650 mAh for size 675 (see Replacement Table).
Important!
- Zinc-air batteries are sensitive to environmental conditions. A decrease in ambient temperature will shorten the battery life. This should be remembered by people, e.g. those who work outdoors in winter.
- An increase in altitude also means a decrease in the oxygen content in the air. Therefore, if you are in the mountains, your battery may last less time.
Remember also:
- After removing the membrane, allow the zinc-air battery to aerate freely (wait about a minute before inserting it into the device).
- Use fresh and efficient batteries when programming your device, as these processes consume the most power.
- Store batteries at room temperature.
- Store batteries in their original packaging. Let them not touch metal objects.
- Do not allow children to play with the batteries.
Other facts related to hearing aid batteries:
- Anode: zinc powder
- Cathode: oxygen (O2)
- Electrolyte: potassium hydroxide (KOH)
- Applications: hearing aids, pagers, electric vehicles
Zinc-air batteries are alkaline batteries (due to the electrolyte used). This is a very interesting type of battery, even if you don't consider the question "how can we use air as an electrode?" (Specifically, oxygen is supplied to the cathode through a hole in the battery and reduced on the surface of the carbon.)
Many electrochemical systems use metal oxide and zinc. The metal oxide is reduced, the zinc is oxidized, and a potential difference is created. This is the principle of the old type of battery used in hearing aids - batteries based on mercury and zinc oxide (mercury batteries are currently discontinued). If we get rid of the metal oxide from them, we are able to double the capacity of the battery - but where to get oxygen then? Exactly. Out of thin air!
The electrolyte in zinc-air batteries is a 20-40% (weight ratio) solution of alkaline hydroxide in water. One of the disadvantages of this solution is the fact that such hydroxides are hygroscopic - they absorb or release water to the environment, depending on the humidity. Both too high and too low humidity have a negative effect on the life of thebattery capacity (selective membranes are the solution here).
Since the battery "does not contain" a cathode (or in any case, the weight of the cathode does not count in the mass of the battery), the energy density per unit weight in zinc-air batteries can reach high values - between 400-500 Wh/kg (for comparison - 99-123 Wh/kg for a cathode with HgO). Unfortunately, the energy density per unit volume remains small.
The shelf life of zinc-carbon batteries before they are exposed to air is about 4-5 years. After activation, their duration of action is not very long, even if they are not used. For these reasons (and also because of the high energy density per unit mass), zinc-air batteries are used to power hearing aids.
An interesting fact for little chemists ;-) How to make a zinc-air battery yourself (in English). Remember to take precautions :):
(1) Rule, A., and Kouba, K. (2013, December). Rayovac hearing aid batteries – important things to know to ensure patient satisfaction. AudiologyOnline, Article 12293.
Popular hearing batteries in the hurt.com.pl store
30 x everActive ULTRASONIC 312 hearing batteries
- reliable zinc-air batteries for hearing aids
- voltage: 1.45V
- Environmentally friendly batteries - mercury-free (0% Hg)
- expiry date: min. 2028
30 x everActive ULTRASONIC 10 hearing batteries
- reliable zinc-air batteries for hearing aids
- voltage: 1.45V
- Environmentally friendly batteries - mercury-free (0% Hg)
- expiry date: min. 2028
30 x everActive ULTRASONIC IMPLANT HD 675 hearing batteries
- A rugged, high-current version of the 675 battery with enhanced performance
- dedicated to cochlear implants and speech processors
- voltage: 1.45V
- Environmentally friendly batteries - mercury-free (0% Hg)
- expiry date: min. 2028
30 x everActive ULTRASONIC 675 hearing batteries
- reliable zinc-air batteries for hearing aids
- voltage: 1.45V
- Environmentally friendly batteries - mercury-free (0% Hg)
- expiry date: min. 2028
-
Świetna obsługa i doskonałe doradztwo
-
bardzo dobrze wyjaśnione, dlaczego bateria na taką samą żywotność (po włożeniu do aparatu) "bez względu" czy aparat jest użytkowany czy tez nie
-
Świat się szybko zmienia , powstają nowe technologie wdrażane w nasze życie a często nic o nich nie wiemy a nawet często trudno znaleźć na ich temat jakąś informację, dlatego wdzięczny jestem i dziękuję ludziom którzy poświęcili swój czas aby opisać i przybliżyć innym "ciekawskim" poznanie tego nowego świata.